
The text of the Sefir Yetzirah, from which the Kabbalah is said to have originated, is supposed by some sources to have been written by Abraham himself on instructions from Shem, the son of Noah, who is also sometimes referred to as Melchizedek among many Hebrew sources. Melchizedek is said by other Hebrew sources to have changed what originally was the sacrifice of animals to God to the offering of bread and wine to Him, perhaps an indication of the movement of human beings from a nomadic hunter-gatherer to an agrarian existence.
Shem, meanwhile, is said to have participated in the spiritual revelation given to Noah by God; and from this, God is said to have orally instructed Abraham to pass on that which he received from God to Shem. So, the authorship of the Sefer Yetzirah is attributed to Abraham for the Hebrews and to Shem for the Gentiles. This suggests that prior to the writing of historical texts (or any texts for that matter), there was a unified spirituality in existence in what was then the known world. This is an amazing thought.
However, other more credible sources attribute the text of the Sefer Yetzirah to around the 1st century BCE, which might indicate the apparent influences of the Neo-Platonic Pythagoreans, Plotinus and the Neo-Platonists, and the neo-Aristotelians on some of the content of the text. The text of the Sefer Yetzirah, in my opinion, is an attempt to resolve the problem of piety and philosophy, the conflict between Jerusalem (piety/theism) and Athens (philosophy/atheism) which is a core problem for the history of thought in the West.

The goal of the knowledge of the Sefer Yetzirah is that one become “a prophet” (c.f. The World #21 card of the Tarot where, at the completion of the journey, the initiate is to have the gift of prophecy or the ability to dwell in both the spiritual and physical worlds simultaneously). Prophecy is “the highest speech”, and one would consider a prophet the “highest” or most complete human being i.e., the most ‘perfect’ human being, the most ‘virtuous’ human being; and we shall see shortly the importance of language and speech in the physical, spiritual and mystical worlds of the Sefir Yetzirah. The prophet is said to be one who dwells in the presence of God, and this has always been considered as the highest end for human beings in both the ancient and medieval worlds of the West. In our interpretation here, dwelling in the presence of God or the Good are understood to be one and the same.
“Kabbalah” means “that which is received”, “that which has been given”, the gift. What is received is believed to be the divine message, the Torah, the divine gift, the salvation and redemption that is the reconciliation of the “perfect imperfection” that is human being with the perfection that is the Divine. That gift which has been received becomes part of one’s heritage or inheritance.
The Sefer Yetzirah outlines an essential “strife” between that which has been received and how that which has been received is understood and interpreted; and this essential strife may be understood as that between the individual and the society or the collective. This is because the Sefer Yetzirah is a philosophical text and its language is the poetry of philosophy. There always has been and always will be strife between philosophy and that which considers itself the established “truth” of the collective, or that upon which the collective (society) is based, be that the canon or doctrine of the religions of those societies or the established opinion of those who hold what knowledge is conceived to be in those societies. Piety belongs to the collective; philosophy belongs to the individual; piety is the exoteric; philosophy is the esoteric.
The Kabbalah is an attempt to interpret that divine message or divine gift and the meaning or significance of that gift. This gift from the god is referred to sometimes as the Tree of Life. This Tree, established in visual form during the Renaissance, is brought to presence to us through language and number. Language and number are gifts from the god, from the Ain Sof. They are not “invented” by human beings but “dis-covered” or “un-covered”, unconcealed. They were always there, only hidden or concealed. This uncovering and revealing is what is called “truth” here.
The Kabbalah’s principles or foundations are based on God’s act of creation ex nihilo in Chapter One of the Book of Genesis in the Western Bible, and one may also understand something of the Kabbalah through the opening words of St. John’s Gospel from that Bible: “In the beginning was the Word, and the Word was with God, and the Word was God. The Same (He) was in the beginning with God. All things (Difference) came into being through Him, and apart from Him nothing came into being that has come into being. In Him was Life, and the Life was the light of human beings. And the light shines in the darkness, and the darkness does not comprehend it.” (John I: 1-5) In the multi-layered universe of the worlds of the text of the Sefer Yetzirah, this is the world of Beriyah, the world of creation of something from no-thing, and in the hierarchy of the worlds of the Sefer Yetzirah, it is below the world of Atzilut, the world of the Divine Ideas or Archetypes, the Sephirot themselves.
I would, cautiously, suggest that the anthropocentric view of the God as the “eternal fiery Father” is not quite right as the God that is characterized by the Sefer Yetzirah, although the God as perceived there is indeed of the element of Fire, particularly when viewed from the left side of the Tree of Life, the side of Severity and Fear. But this is only one of His elements. Being infinite, ineffable, and unnamable, perhaps He is what we mean by Life itself, and therefore images of Him or uttering His true Name is taboo in Hebrew and Islam since the utterance of a name or the production of an image “solidifies” or ossifies that which is named. The early Greek philosopher, Heraclitus, once said: “the god who sometimes does and sometimes does not wish to go by the name of Zeus” when He is called upon since He chooses to appear in and under many forms and names.
I am always astounded, for instance, by other sects of Christians who accuse Catholics of being pagans because these other sects think the Catholics worship statues i.e.; they are idol worshippers. The statue is, of course, not the Being him/herself that is being supplicated, but a mediary between the person at prayer and the Being they are calling upon for aid, just as all Art is a mediary between human being and Life itself. The statue helps focus their prayer. I am also cautious because I remember the lines from the English poet William Blake who said in his poem “Auguries of Innocence”: “God appears and God is light/ To those poor souls that dwell in night/ But does the human form display/ To those who dwell in realms of day.” Referring to this I must say: I simply do not know; but I do know the Sefir Yetzirah is closer to Blake than to the traditional religions and their interpretations be they Hebrew or Christian. Also, Blake’s meaning is present in many mythologies and religions throughout the world. It is sometimes called the “mystical tradition”. It is what is called esoteric, that which is hidden or occult or merely that which is ‘private’, and it is contrary to the exoteric which is for ‘public viewing.’
God, in the Sefer Yetzirah, is said to have created His world with three “books”. With these three “books” (Heb. Sepharim, Gr. logoi): 1. text (Heb. Sepher, Gr. Logos, speech that is written or spoken i.e. rhetoric) with 2. number (Heb. Sephar, Gr. arithmos) and with 3. communication, speaking to one another (Heb. Sippur, Gr. Dialectic?), human beings are called upon to “dis-cover” and “un-cover” the mysteries of the created universe. The world is meant to be read as text and upon this reading communicated to others.
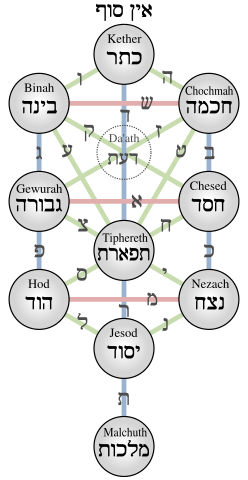
The Tree of Life is said to be composed of 10 Sephirot or the Ten Emanations of God (referred to as the Ten Commandments in the Torah). “Emanation” is the action of flowing from a source. Perfume emanates from a flower, for instance. The Sephirot are connected by paths or channels created by the 22 letters of the Hebrew alphabet, thus 32 paths in total, 10 Sephirot + 22 paths. The 22 paths are the letters of the Hebrew and early Greek alphabets (which are both said to derive from the Aramaic language), and the 10 Sephirot also represent the ten fingers of the human body. The human form is considered the microcosm of the macrocosm of the whole of Creation (again referencing Blake’s ‘augury’ here.)
The importance of “grasping” and “being able to grasp” is present in the text of the Sefer Yetzirah. With the letters comes speech (what the Greeks understood as logos), and with the fingers come numbers which are used to “count on” or to calculate. The paths are described as channels through which the “waters” of the spiritual flow downward (One must be “born again of the water and of the spirit” in order to rise up or go against the Necessity of gravity which pulls downwards). Water, by nature, flows downward; to “flow” upward, water requires fire or needs to become “air”, literally clouds. These movements of the spiritual as ascent and descent are the essential feature of the Tree of Life. The downward movement is creation and the upward movement is decreation in the interpretation offered here.
“Speaking to one another” and the Greek word dialectic have undergone great changes over the centuries. The word dialectic literally means “conversation between two or three persons” (esoteric), not two or three hundred persons for that would make it rhetoric, the speech of one to many (exoteric). The original dialectic, the conversation between friends, has been permutated into what is now known as Hegelian dialectic (thesis, antithesis, synthesis) and to Marx’s “dialectical materialism” where the original dialectic of the “sharing of the spirit” is attributed to physical matter through human beings’ making that matter or material “valuable” through their labour and through their “absolute knowledge” of that material which they have made. This making of “value” is the origin of our concept of “values” which has derived from the disappearance of God and the oblivion of eternity in order to place human beings, falsely, at the centre of the world. “Values” and their historicity have come to replace “morality” and “ethics” in our lexicons. The Greeks and the early Hebrews had no “values”.
The Tree of Life of the Kabballah

The letters and the paths associated with the Sephirot correspond to the 22 Major Arcana of the Tarot, and the emanations of the Sephirot correspond to the symbols and images presented in the cards, from the sacred to the profane; that is, the objects and situations that we encounter within our worlds correspond in their true natures to the numbers and images “revealed” in the cards when the cards are interpreted correctly. The cards, composed of letters and numbers, are intermediaries between the individual and the world we live in. They are tools to assist us in the overcoming of the distinction between mind/body, soul/body, and the self/world. All that is known (the Greek word gnosis) is brought to presence (ousia) through language and number, or through Word. The desire to know is urged by the ‘need’ and ‘fullness’ that is Eros. Both logos and eros are to be found in the Sephirot Tiferet #6, for all the paths of the other Sephirot lead through Tiferet with the exception of Malkhut.
A most important point to note is that the creation of the world is not an “expansion” from God but a withdrawal of God. In making the universe, God allows something other than Himself to be and yet, paradoxically, it is at the same time Him since He is One and the Whole. This Otherness and withdrawal of God signifies both His presence and His absence in His creation. We might consider this making of God analogous to the making of the great artist (and I mean only great art here) where the artist withdraws to allow something other than him/herself to be, something which is at the same time, part of him/herself and yet not part of him/herself. One could carry it even further and make an analogy to a woman giving birth to a child. A woman’s giving birth is her great recognition of Otherness. It is her desire for the Incarnation of the Divine, and this desire or urge begins with Eros. It is this withdrawal of God, His allowing something to be other than Himself, that is the argument against the Gnostics who see the world’s creator as somehow an evil Demiourgos; yet, as we will see later, what we understand as ‘evil’ is a constant presence among the things that are and it impacts how Eros is to be understood.

The Greek word demiourgos means “a public or skilled worker” i.e., the politician or the techne, one who is skilled at making something from something and for someone else. In other languages, the demiourgos is “the blind god” or “the foolish one”, one who is ignorant of the gods or opposed to them i.e., the malevolent one. In many Gnostic texts, the demiourgos creates the physical world and the human beings in it. He creates followers who preside over the material world and who present obstacles to the soul seeking to ascend from it. The Fool #0 and The Magician #1 may be said to correspond to the demiourgos of the Gnostics and equal the numbers 01 and 10 respectively. In the Tarot, this shows their connection with The Wheel of Fortune #10.



